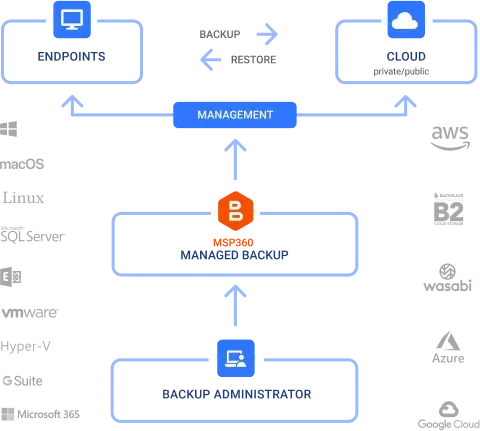
Data Backup & Recovery
Data backup and recovery refer to the process of creating and storing copies of digital data in a secure location and the ability to restore that data in case of data loss, accidental deletion, hardware failure, software corruption, natural disasters, or other data-related incidents.
Data backup involves making copies of data and storing them in a separate location from the original data. This can be done using various methods, such as local backups to external hard drives, network-attached storage (NAS) devices, or tape drives, or cloud-based backups to remote servers via the internet.
Data recovery, on the other hand, is the process of restoring the backed-up data to its original state after a data loss event has occurred. This can involve retrieving data from backups and transferring it back to the original system or device, or to a new system or device.
Data backup and recovery are critical components of an organization’s data protection strategy. They are essential for ensuring business continuity, protecting against data loss, and minimizing downtime in case of data-related incidents. Here are some key considerations for data backup and recovery:
- Regular and automated backups: It’s important to establish a regular backup schedule and automate the process to ensure that critical data is consistently backed up. This can help prevent data loss and ensure that recent data is available for recovery.
- Offsite backups: Backing up data to an offsite location, such as a remote server or a cloud-based storage service, provides an additional layer of protection in case of physical damage or loss of the original data location.
- Multiple backup copies: Creating multiple copies of backups and storing them in different locations can help mitigate risks of data loss. This can include creating multiple copies in different physical locations or using different backup methods.
- Data encryption: Encrypting backup data can add an extra layer of security and protect against unauthorized access to sensitive information.
- Testing and verification: Regularly testing and verifying the integrity of backup data is crucial to ensure that the data can be successfully restored when needed.
- Disaster recovery plan: Having a well-defined and documented disaster recovery plan that outlines the steps and procedures for data recovery in case of a data loss event is critical for efficient and effective data recovery.
- Employee training and awareness: Educating employees about the importance of data backup and recovery, and providing training on how to properly back up and restore data, can help prevent accidental data loss and improve overall data protection.
Data backup and recovery are essential components of modern IT management, and organizations of all sizes should have a comprehensive data protection strategy in place to safeguard their critical data and ensure business continuity in case of data loss events.